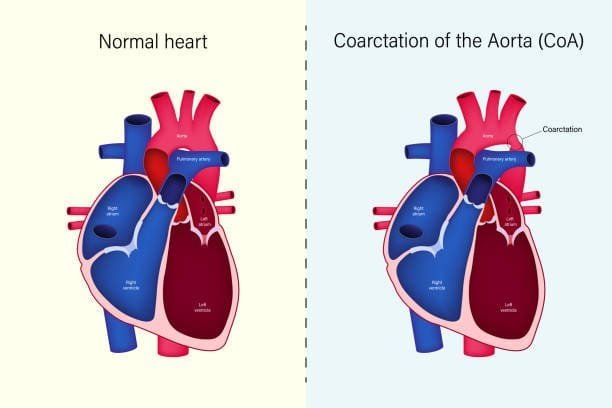
Congenital Heart Disease
It is a term that may sound very serious; however, it is about time that we educate ourselves with this disease that affects numerous babies per year. Some of the questions that will be discussed in this article include: what is congenital heart disease, its causes, how it can be known, the available treatment, and ways of preventing it. Sooner or later, you will, perhaps, come up with a sharper consciousness of this heart condition.
Congenital heart disease can be defined as one of the heart diseases that is present at birth. These imperfections can reach the point where the architectural or functional development of the heart of the child is compromised. While it may sound quite catastrophic, millions of children with congenital heart disease can still live rather energetic lives due to advances in medicine.

Congenital heart disease is a condition or group of conditions where the heart is either structurally or functionally abnormal at birth. Congenital heart disease refers to all forms of abnormalities of the heart that one is born with.
But, of course, on some occasions, congenital heart disease is, indeed, the combination of some of the deformities.
What should not be forgotten is that congenital heart disease cannot be a single disease but a general term for different heart problems. Some congenital heart diseases are mild and do not require intervention, while there are complex congenital heart diseases that need multiple interventions for a long time.
Causes:
It is very difficult to try and understand what leads to congenital heart disease because, in general, there is no known cause for it. Nonetheless, scientists have recognized a few factors that might expand the chances of a child having congenital heart disease:
Genetic variables:
A few of the heart imperfections can be bought or are a consequence of an ailment or the aging process. In the event that a parent or kin has congenital heart disease, there are better possibilities of the child being conceived with it as well.
Chromosomal irregularities:
Some congenital diseases, particularly Down syndrome, are associated with an increased risk of inherent cardiac abnormalities.
Environmental elements:
Some substances that are tolerated when ingested during pregnancy, like liquor, specific medications, or poisonous substances, can increase the possibility of congenital heart disease.
Maternal medical issue:
That is why some of them might have an increased prospect of having a child with congenital heart disease if they have diabetes weight or rubella contamination during pregnancy.
Maternal age:
Younger bearing age or older than 30 years might increase the risk of having a baby with congenital heart disease slightly.
It’s important to note that, generally speaking, it occurs almost without symptoms. Parents should not blame themselves if ever their child is born with a heart disorder.
It is also important to note that it comes with some side effects, which may include:
The manifestations of congenital heart disease vary generally depending on the type and severity of the defect. Some children may have hints immediately after birth, and some children probably will not show any signs or side effects for several days. Here are a few disease signs to pay special attention to:
Babies and Newborn Children:
- Peripherally constricting cherry red to bluish discoloration of the skin, lips, and fingernails (cyanosis)
- Dyspnoea or difficulty in getting, staying, or stopping breath.
- Lack of proper care and weight gain
- Sweating, particularly when taking care of
- Fatigue or sluggishness
In More Established Kids:
- Dyspnea, which is a condition whereby one or more may experience difficulty breathing while in action or during exercise.
- Further, quickly getting tired while actively working.
- Oedema involving the right hand, lower legs, or feet
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
- Dizziness or swooning
It means a lot to take note of that not all children and youngsters born with it will exhibit typical signs. Fetal echocardiogram: For instance, this ultrasound of the child’s heart can identify a number of heart diseases before birth.
- Physical assessment: After birth, the specialists remain nearby, listening to the child’s heart and lungs, and looking for signs of a heart defect.
- Pulse oximetry screening: This simple, easy test measures the oxygen amount in the blood of an infant.
- Cardiac catheterization: Here, a small cylinder is placed into a vein and guided into the heart for tissue-specific imaging and stress measurements.
The fact is that early conclusion is important to manage it, actually.
Treatment Options
For congenital heart disease, the therapy depends on the type and severity of the defect. Some of the couple of gentle imperfections possibly will not need any sort of treatment, and others would need immediate treatment. Here are some normal treatment choices:
- Watchful pausing: In gentle deformity cases, the specialists are in a position to recommend a normal checkup to monitor the condition.
- Medications: Some of the medications can help in managing the symptoms and improving heart capacity.
- Catheter methodology: Several defects can be repaired by using flimsy cylinders that are inserted through the veins, avoiding the need for invasive surgeries.
- Open-heart medical procedure: It wouldn’t be surprising if more mind-boggling deformities may need to be fixed with great care.
- Heart transfer: In a few rare, major circumstances where such treatments are not possible, a heart relocation might be needed.
- Lifestyle changes: As the children with congenital heart disease grow up, they may need to adapt to various lifestyle changes to be healthy.
It means quite a lot to observe that treatment for congenital heart disease is often advancing. Of course, a lot of such people with inborn heart deserts require periodic examinations throughout their lifetime for the assessment of heart health.
Life with a congenital heart ailment
Due to modern medical dazzle, most children with it survive to adulthood. Be that as it may, living with it frequently requires a few exceptional contemplations:
- Regular clinical consideration: The basic check-ups must include cardiology appointments.
- Exercise: Though the majority of the people with it perform exercises, they have to adhere to certain guidelines.
- Diet: As such, there are certain factors that support a heart-solid eating plan for general cardiovascular health.
- Pregnancy: Women with congenital heart disease should discuss with their primary care physicians before pregnancy.
- Emotional help: So as to live with said affliction is difficult, and the use of psychological support could be ethical.
There are specifics that have been associated with lesser probabilities to develop congenital heart disease, where they include;
While not all instances of congenital heart disease can be forestalled, there are steps that hopeful moms can take to lessen the gamble:
- Maintain great pre-birth care: It is good to make standard check-ups during pregnancy.
- Take folic corrosive: There are some birth deserts that this B nutrient can help prevent.
- Get inoculated: Some illnesses in pregnancy can increase the risk of congenital heart disorders. Something wrong with the blood can widen the risk of inherent heart problems.
- Avoid certain prescriptions: There are a couple of medications that raise the danger of heart deserts. Always communicate with your PCP regarding any medicines that you are taking.
Conclusions
Congenital heart disease is a fascinating disease; however, with proper diagnosis and proper medical treatment, people with such heart defects can lead normal active lives. In the event that you are planning a baby or assume that you have a baby suffering from congenital heart disease, remember that you are among the lucky ones. There is a host of assets and care groups available to help you undertake this journey.
Since how we might interpret congenital heart disease progress, the treatment options and executive techniques also continue to evolve. Even though it could very much be a debilitating condition to deal with, many people diagnosed with congenital heart disease lead full and enriching lives and make the most of every moment.
FAQs
Can congenital heart disease be restored?
Sometimes numerous inborn heart deformities can be corrected; however, the vast majority of children with congenital heart disease require ongoing care.
Is it worthy of note whether it is safe for ladies with congenital heart disease to get pregnant?
Although women with congenital heart disease have the opportunity to give birth to a healthy child quite often, they need to consult with their doctor. Nonetheless, it is important to note that, any potential dangers should be talked to a cardiologist and high-risk obstetrician before conceiving and plan the right course of action.