Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a severe clinical condition that affects a vast number of people worldwide. This continually spiraling chaotic state, characterized by progressive decrement in the kidney function, can touch an individual’s quality of life dramatically.
In this article, the reader will get to find out more about the causes and effects of chronic kidney disease, its treatment options, and how to prevent the situation.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease?
Chronic kidney disease refers to a long term condition that affect the kidneys and/or reduce their aptitude to filter waste and excess fluids from the body. The sickness may cause difficulties as it progresses; these include high blood pressure, pallor, and, in the extreme case, renal failure.
Risk Factors of Chronic Kidney Disease
Knowing the risk factors of chronic kidney disease is crucial for both prevention and good management. Some essential factors may include:
- Hypertension: This means that if the hypertension is not well managed, it has the potential of damaging the already delicate veins in a kidney.
- Glomerulonephritis: This is an inflammation characterized by the damage of kidney’s purifying units called glomeruli.
- Polycystic kidney illness: An acquired condition characterized by the development of various cysts in the kidneys.
- Obstruction of the urinary tract: It is seen that some conditions, such as hypertrophy of prostate, kidney stones, or malignancies, can obstruct the urinary tract and result in chronic kidney disease.
- Repetitive kidney infections
- Obesity
- Age over 60 years
- Smoking
- History of Kidney Condition in the Family
Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
Some of the challenges with diagnosing chronic kidney disease early are that some of the symptoms of the condition rarely show until the disease has become advanced. Nonetheless, a few kidney disease symptoms to keep an eye out for include:
- Exhaustion or fatigue
- Swelling, including the lower legs or feet.
- Decrease in the quantity and/or quality of the urine or difficulty in passing the urine.
- Unexplained weight reduction
- Queasiness and heaving
- Loss of appetite
- If for any reason liquid develops in the lungs, this is what may be referred to as short of breath.
However, care should be taken and examination done properly once we notice these because this could be also attributed to other conditions. Education for chronic kidney disease screening that can be obtained with simple physical examinations and routine blood tests.
Diagnosis and Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
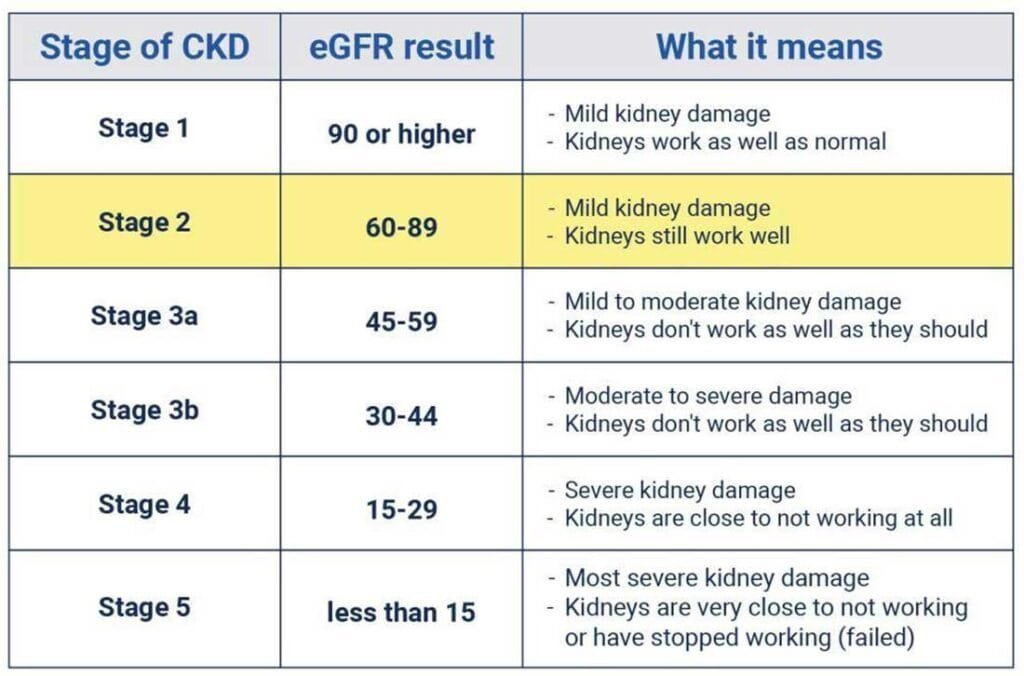
Diagnosis of chronic kidney disease has mostly been done through blood tests, urine tests, and imaging audits. Some of the values used in calculating stages of the disease involve renal filtration rating, or more commonly known as the glomerular filtration rate(eGFR), simplified and known as a vital sign of kidney capability.
- Stage 1: Normal eGFR of 90 or more. This stage means your kidneys are working normally and there only minor damages
- Stage 2: mild kidney damage with eGFR between 60 and 89. At this stage your kidneys are still working well
- Stage 3: Usually 3a (eGFR between 45 and 59) and 3b (eGFR between 30 and 44). At this stage, we have moderate to severe kidney damage.
- Stage 4: Severe kidney damage with eGFR between 15 and 29
- Stage 5: The most severe damages of kidneys and at this stage eGFR is below 15
Chronic Kidney condition Management
There is no remedy for ongoing kidney illness; however, different administration choices for the sickness can assist in adapting to secondary effects or lessen the progession of the disorder.
In this way, the treatment program depends on the essential explanation and the phase of the disease.
- Prescriptions: They might utilize medications to oversee circulatory strain, diabetes, cholesterol, pale tone, hypertension, etc.
- Dietary changes: A kidney-accommodating eating routine, frequently a low-protein, low-sodium, and low-potassium diet, can assist with diminishing the damage on the kidneys.
- Way of life changes: smoking cessation, managing body weight and working out consistently may all add to the kidney wellbeing.
- Dialysis: In the high-level phase of kidney damage, it could be important to flush waste out of the blood with the assistance of dialysis.
- Kidney transplant: In a particular kidney-unwell patient with ESRD (End-stage renal disease), kidney transplant could end up being the best option.
It is currently accepted to be basic for individuals with persistent kidney disease to have one-on-one consultation with their clinician to organize an individual therapy plan.

A Word on Prevention Methods
While not all occasions of ongoing kidney sickness can be prevented, there are a couple of steps you can take to lessen your bet:
- Oversee essential conditions: To oversee diabetes and hypertension, take meds, practice good eating habits, and embrace better living propensities.
- Keep a sound way of life: consume a healthy amount of food, exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy body weight.
- Stop smoking: It is also clearly seen that smoking leads to a destruction of the kidney and raises the risk of kidney diseases.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive consumption of alcohol is not good for the kidney and liver of human beings.
- Remain hydrated: Drinking much water supports your kidneys in their function of removing waste from the body.
- Stay away from too much over-the-counter pain medication: Use of certain painkillers for a long period of time is dangerous to your kidneys.
- Get routine check-ups: A basic blood and urine examination go a long way in diagnosing the kidney complications early.
Conclusion
Chronic kidney disease is a challenging disorder that affects a people all over the globe. If we can understand the root causes of it, become aware of the consequences or side effects, and look for ways on how to ensure that we can actively monitor and maintain proper care for kidneys, then perhaps we can work on finding ways on how to minimize the impact of this disease on as many people and society in general as possible.
FAQs
Can chronic kidney disease be reversed?
Often, chronic kidney disease can’t be fully reversed. Prompt identification and appropriate therapy can delay its progression and occasionally halt further degeneration.
The point is to name the underlying issues and if any, such as diabetes or hypertension, obesity, and to else institute significant life modifications.
In any case, when serious kidney damage has occurred, the main goal is to manage symptoms and avoid complications.