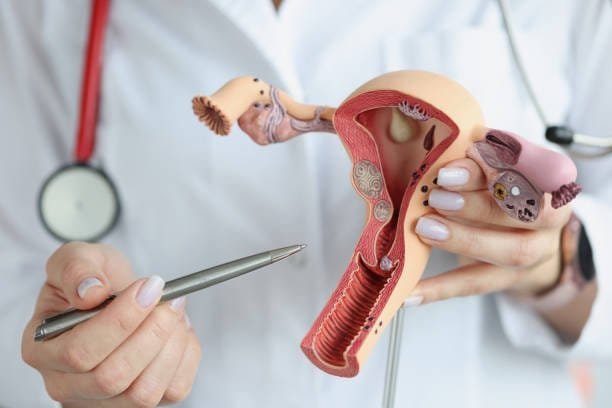
Cervical cancer
It is a severe condition that affects women around the globe. It is an illness in which some irregular cells develop in the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that links the uterus to the vagina. It is one of the most common cancer in women around the world and if diagnosed early, the chances of recovery are high.
Here in this article, we are going to deep dive into the world of it, knowing its causes, impacts, possible actions, and prevention measures.

What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer occurs when some cells in the cervix begin to develop and then reproduce in an abnormal way. These abnormal cells can invade surrounding tissues and, in the long run, can migrate to other parts of the body. The vast majority of cervical cancer cases result from particular strains of human papillomavirus (HPV), that can be transmitted through skin contact or sexual contact.
Causes
It is even more important to comprehend the causes of cervical cancer in order to counteract them and identify them at the earliest stage possible. While HPV is the essential driver, a few different elements can build a lady’s gamble of fostering this infection:
Human Papillomavirus (HPV):
This one is in most cases the main cause for cervical cancer. In some cases the infection can clear by itself. Nevertheless, in some people persistent HPV infection can cause cell alterations, which could lead to disease after some time.
Risk factors
The cancer can sometimes develop without known risk factors but sometimes it’s associated to specific conditions. Some of these conditions are:
Smoking:
Female smokers are approximately two times sooner to establish cervical cancer than non-smokers. Tobacco side-effects have also been established in the cervical bodily fluid of the ladies who are smokers.
Compromised immune system:
Factors that compromise the immune system, such as HIV, help raise the danger of HPV disease progression to cervical cancer.
Long-haul utilization of oral contraceptives:
A couple of studies propose that long-term utilization of conception prevention pills can increase the risk of cervical cancer by a negligible degree.
Multiple pregnancies:
Full-term pregnancies, particularly three or more pregnancies in ladies, extend the chance of having it.
Early sexual activities:
Leaving alone turning out to be physically dynamic quite early on creates the risk of HPV contamination.
Numerous sexual partners:
If a man has various sexual partners or if his associate has had various sexual partners, the danger of getting HPV disease increases.

Signs and Symptoms
Beginning phase it does not produce any noticeable side effects; this is the reason why regular checks are very useful. In any case, as the malignant growth advances, the accompanying side effects might show up:
- Strange vaginal bleeding: This can include between periods, after intercourse, or after the menopausal stage.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge: It could be watery, have a bad odor, or have a vomit-like smell.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain: Pelvic area pain during sexual intercourse can therefore be regarded as an indication of advanced cervical cancer.
- Back or leg torment: When the cancer begins to metastasize, it may result in pain in the back, legs, and pelvis.
- Weakness: Lack of energy or lethargy common for different diseases is one of the symptoms of it .
- Weight and appetite reduction: It is also important to note that weight loss may occur at random as the malignant growth progresses.
- Trouble peeing or pooing: In advanced phases, it can compress close by organs, causing problems with urination or defecations which may include pain or bleeding.
What one needs to note concerning the side effects is that they may also be caused by other causes. But if you have any of these side effects, it is appropriate to consult a medical services provider for a proper evaluation.
Diagnosing the disease
- Pap smear: This screening test is used to recognize any changes in cervical cells that may indicate precancerous changes.
- HPV test: This test reflects any straining of high-risk HPV associated with cervical cancer.
- Colposcopy: A position that lets the specialist to closely examine the cervix even more.
- Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is uninvolved from the cervix to fulfill a research-based check-up for the assessment of research centers.
- Imaging tests: CT scans, sweeps, X-rays, or even PET output may be used to determine whether the disease has progressed.
Once it is analyzed, it is stratified from I to IV based on the progress made in the spread of the sickness. The above arrangement determines the most appropriate one for treatment.
Treatment Choices
Medical procedure:
Signs that may indicate adequacy in the beginning phase it includes medical procedures. Options that are offered include excision of the malignant tissue only up to evacuation of the entire uterus.
Radiation treatment:
This utilizes high-energy beams to kill disease cells. It is often cast-off either singly or in combination with other drugs.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapeutic medications are prescribed for eliminating sine as malignant growth cells in every part of the body. It is often utilized together with radiation therapy to treat more advanced stages of cervical cancer.
Designated treatment:
These medications work at particular vulnerabilities in malignancy cells and are usually less destructive to healthy cells than conventional chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy:
This fairly novel procedure permits the body’s dangers to detect and eradicate cancer cells.
Avoidance
Forestalling Cervical cancer is conceivable through a mix of immunization, standard screenings, and way of life decisions:
HPV vaccine inoculation:
The HPV antibody is able to protect from the kinds of HPV that most frequently lead to cervical cancer. This is for the two young ladies and young men before they get to be physically active in their youthful prime.
Normal screenings:
Pap spreads and HPV tests can identify alterations that are precancerous prior to turning into cervical cancer.
Safe sex works on:
Anal sexual conduct, oral sex, and vaginal penetrative sex with more than one accomplice build up the danger of HPV disease; in this way, utilization of condoms and limit of partners diminishes the danger of this sickness.
Stopping smoking:
Smoking increases the risk of cervical cancer; thus, quitting it may reduce your risk by half.
Keeping a solid way of life:
Moderate and sound eating routine, ordinary exercise, and sound weight all contribute to decreased hazards again. Cervical cancer.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is a significant aspect of wellbeing that is a colossal worry to a great many individuals, yet with the right data and preventive methodologies, its impacts can be tremendously reduced. Preventable measures such as simple checkups, vaccinations, and healthy lifestyle choices are a major prevention of this disease.
As previously mentioned, remember that the cancer is curable at any given point in time, especially when detected in the early stage. It may sound paradoxical, but the idea is that if you keep educating yourself and reading about your health, you are effectively lowering your chances of cervical cancer, and in case it happens, get the problem solved when it’s still easy.
FAQs
Can the above conditions be relieved?
However, cervical cancer can even be cured quite often, especially if it is distinguished and treated at a very early stage. Surgical treatment of cervical cancer, which is known as Wertheim’s operation (also known as radical hysterectomy), is 100% effective if done correctly and early. However, the five-year endurance rate for restricted cervical cancer (a disease that hasn’t spread past the cervix) is more than 90%.
Is cervical cancer genetic?
For example, a couple of ladies could develop illnesses that make them much less prepared to avoid HPV contamination, and this is most of the time responsible for cervical cancer. Moreover, if a close kin (for instance, a mom or sister) has had cervical cancer.